Archive for the ‘System Administration’ Category
February 29th, 2012
Windows 7 includes a little-known new feature called Virtual Wi-Fi, which effectively turns your PC or laptop into a software-based WiFi router.
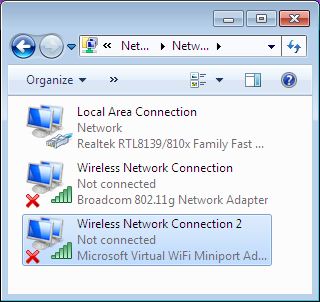
Any other Wi-Fi-enabled devices within range a desktop, laptop, an iPod perhaps will “see” you as a new network and once logged on, immediately be able to share your internet connection.
This will only work if your wireless adapter driver supports it. Check with your adapter manufacturer and make sure you’ve installed the very latest drivers to give you the best chance.
Once you have driver support then the easiest approach is to get a network tool that can set up virtual Wi-Fi for you.I go for “Virtual Router”. Virtual Router is free easy to use and you can share your internet connection very quickly. You can find the software in the net.
The idea behind the Virtual Wifi is simple, the operating system can virtualise any compatible wireless adapter to make it appear as though you’ve as many additional adapters as you need.
Another process of setup without installing any Additional Software:-
The set up process is simple and for this you have to deal with Command prompt. Click Start, type CMD, right-click the Cmd.exe and select “Run as Administrator” (How to run as Administrator) .Now type the following command
netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allow ssid=MyNet key=MyPassword
press enter. Replace “MyNet” with the name you’d like to use for your custom network, and “MyPassword” with a password that’s a little harder to guess.
After that type the command
netsh wlan start hostednetwork
Press enter.
Now go to Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Centre > Change Adapter Settings,
right-click your internet connection and select Properties.
Click the Sharing tab, check “Allow other network users to connect.”. choose your virtual Wi-Fi adaptor
December 14th, 2011
In previous versions of PuTTY, 0.59, 0.60 and 0.61, the password used to log on to an SSH2 server was retained in memory.
The password was then retrievable by other programs that could read the memory, or could be found in swap files and crash dumps.
The update also fixes non-security-related errors including correcting the rendering of underlines and VT100 line-drawing characters, removing a spurious GSSAPI authentication message, restoring saved sessions, and closing a leak of file mapping handles when authentication failed.

Details of the changes are in the release notes. Pre-built binaries and source code for the MIT-licensed PuTTY are available to download.
November 8th, 2011
Mozilla announced today the official release of Firefox 8
The built-in search box in Firefox’s navigation toolbar has been extended to support Twitter searches. Users can now select Twitter from the drop-down list of available search engines. Mozilla partnered with Twitter earlier this year to release a special build of Firefox that ties into the social network. The search box integration from that custom build is now part of the official Firefox release.
Another noteworthy user-facing feature in Firefox 8 is stricter control over side-loaded add-ons. Mozilla is cracking down on third-party applications that install add-ons in Firefox without the user’s knowledge or permission.
If Firefox 8 detects side-loaded add-ons when it starts, it will disable them by default and display a prompt asking the user if they want the add-on to be enabled. This will help protect users from invasive toolbars and other unwanted cruft.
In addition to these new browser features, Firefox 8 also has some improvements under the hood. The browser’s HTML rendering engine has gained support for cross-origin resource sharing, a feature that will allow a website to load WebGL textures from other sites. WebSockets also got a boost in this release with an updated implementation that conforms with the latest draft specifications
Users can download Firefox 8 from Mozilla’s website. The new version will also be rolled out to users through the stable update channel.
November 4th, 2011
To enable hibernation. To do this, follow these steps:
| 1. |
Click Start  , click All Programs , and then click Accessories . , click All Programs , and then click Accessories . |
| 2. |
Right-click Command Prompt , and then click Run as administrator .
 If you are prompted for an administrator password or for a confirmation, type the password, or click Allow . If you are prompted for an administrator password or for a confirmation, type the password, or click Allow . |
| 3. |
At the prompt in the Administrator: Command Prompt window, type powercfg -h on |
If you want to disable Hibernation completely
At the prompt in the Administrator: Command Prompt window, type powercfg -h off
September 29th, 2011
Firefox 7 isn't just about speed, there's also a long list of security patches. Surprisingly, a fix for the SSL BEAST attack is not one of them.
Mozilla is patching it's Firefox Web browser for at least 10 vulnerabilities, seven of which are rated as being "critical." Firefox 7 was released on Tuesday offering users the promised of improved performance and better memory usage.
On the security front, the Firefox 7 release provides a critical fix for what Mozilla describes as, "Miscellaneous memory safety hazards."
"Mozilla developers identified and fixed several memory safety bugs in the browser engine used in Firefox and other Mozilla-based products,"
Mozilla stated in its advisory. "Some of these bugs showed evidence of memory corruption under certain circumstances, and we presume that with enough effort at least some of these could be exploited to run arbitrary code."
There is also a critical fix for an interesting flaw that could have been triggered by having a user hold down the 'Enter' key. By holding
down the key, code could potentially be installed without a user's knowledge.
"Mariusz Mlynski reported that if you could convince a user to hold down the Enter key — as part of a game or test, perhaps — a malicious
page could pop up a download dialog where the held key would then activate the default Open action," Mozilla warned.
Other critical flaws that are fixed in Firefox 7 include potentially exploitable crashes in WebGL graphics and the YARR regular expression
library. Firefox 7 also provides a fix for a high impact flaw where cross-site scripting (XSS) could have been enabled via plugins.
There is also a fix in Firefox 7 for a flaw rated as "moderate" that is triggered by the motion of a device. Mozilla's advisory noted that a recent research paper detailed how it would be possible to inferring keystrokes from device motion data on mobile devices.
"Web pages can now receive data similar to the apps studied in that paper and likely present a similar risk," Mozilla warned. "We have decided to limit motion data events to the currently-active tab to prevent the possibility of background tabs attempting to decipher
keystrokes the user is entering into the foreground tab."
SSL BEAST
While Firefox 7 addresses multiple security issues, it is not taking specific aim at the recent disclosure of potential SSL vulnerabilities. Overall, Mozilla has publicly noted that they do not believe Firefox to currently be at risk from the SSL BEAST attack
September 29th, 2011
SSL is a critically important part of Internet security and it has come under increasing scrutiny in recent months. Last Friday, a pair of security researchers demonstrated a new attack called SSL BEAST at the ekoparty security conference in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Researchers Thai Duong and Juliano Rizzo leveraged weaknesses in cypher block chaining (CBC) in order to exploit SSL.
"The SSL standard mandates the use of the CBC mode encryption with chained initialization vectors (IV)," the researchers wrote in a white paper detailing their research. "Unfortunately, CBC mode encryption with chained IVs is insecure, and this insecurity extends to SSL."
Duong and Rizzo noted the CBC vulnerability can enable a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks against SSL to decrypt and obtain authentication tokens.
"The novelty of our attacks lie in the fact that they are the first attacks that actually decrypt HTTPS requests by exploiting cryptographic weaknesses of using HTTP over SSL," the researchers stated.
While the SSL BEAST attack is a cause for concern, there are already technologies in place to help mitigate the risk. For one, the BEAST attack only affects the TLS 1.0 version of SSL and not later versions. One vendor that leverages a non-vulnerable version of TLS is the Tor onion router project which provides a degree of anonymyity and privacy to users..
"Tor uses OpenSSL's empty fragment feature, which inserts a single empty TLS record before every record it sends," the Tor project noted in a blog post. "This effectively randomizes the IV of the actual records, like a low-budget TLS 1.1. So the attack is simply stopped."
Google's Chrome Web browser has also taken steps to mitigate the risk as well.
"Chrome has already addressed the issue and the fix on the browser side is quite simple and elegant," ISC SANS security research Mark Hofman blogged. "We'll see the other browsers implement something similar over the next few weeks. That doesn't fix the protocol, but it will help address the immediate issue of clients being attacked in this manner."
Google engineer Adam Langely blogged that Google's own servers are also somewhat protected from the SSL BEAST attack since they use a cipher that doesn't use CBC.
While Google has already taken steps to protect its users, Microsoft sees the risk as being low.
"Microsoft is aware of the industry-wide SSL 3.0 / TLSv1.0 issue demonstrated at a recent security conference which we believe presents low risk to our customers and to the Internet," Jerry Bryant, Group Manager, Response Communications, Microsoft Trustworthy Computing said in a statement emailed to InternetNews.com. "Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 support TLSv1.1 and TLSv1.2 but due to compatibility issues with many web sites, are not enabled by default."
2011 has not been a good year for SSL. SSL has come under fire due to the exploit of a pair of certificate authorities. Both Commodo and DigiNotar were exploited this year leaving big sites including Google and Mozilla at risk.
 , click All Programs , and then click Accessories .
, click All Programs , and then click Accessories .  If you are prompted for an administrator password or for a confirmation, type the password, or click Allow .
If you are prompted for an administrator password or for a confirmation, type the password, or click Allow .