Archive for the ‘Networking’ Category
November 26th, 2013

“Don’t tell anyone that I’m free”
WinSSH
Update (10/July/2016): OpenSSH (7.2p2) Server for Windows (7.2p2 is latest version of OpenSSH)
OpenSSH (6.4p1) Server for Windows (Previous version of OpenSSH)
General Features:-
* Security, if you want to access your Windows Machines cmd shell with full security.
* Windows NT Service Support
* Full install about 12mb, installer under 8mb (Including Cygwin dependencies)
* Windows Command Prompt support for SSH Terminal
* SCP/SFTP server support (secure file transfer)
* Command-line clients included Read the rest of this entry »
February 29th, 2012
Windows 7 includes a little-known new feature called Virtual Wi-Fi, which effectively turns your PC or laptop into a software-based WiFi router.
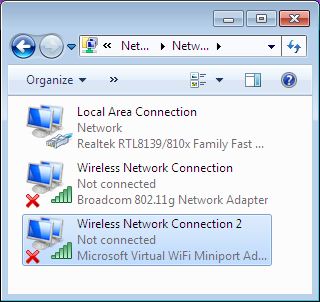
Any other Wi-Fi-enabled devices within range a desktop, laptop, an iPod perhaps will “see” you as a new network and once logged on, immediately be able to share your internet connection.
This will only work if your wireless adapter driver supports it. Check with your adapter manufacturer and make sure you’ve installed the very latest drivers to give you the best chance.
Once you have driver support then the easiest approach is to get a network tool that can set up virtual Wi-Fi for you.I go for “Virtual Router”. Virtual Router is free easy to use and you can share your internet connection very quickly. You can find the software in the net.
The idea behind the Virtual Wifi is simple, the operating system can virtualise any compatible wireless adapter to make it appear as though you’ve as many additional adapters as you need.
Another process of setup without installing any Additional Software:-
The set up process is simple and for this you have to deal with Command prompt. Click Start, type CMD, right-click the Cmd.exe and select “Run as Administrator” (How to run as Administrator) .Now type the following command
netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allow ssid=MyNet key=MyPassword
press enter. Replace “MyNet” with the name you’d like to use for your custom network, and “MyPassword” with a password that’s a little harder to guess.
After that type the command
netsh wlan start hostednetwork
Press enter.
Now go to Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Centre > Change Adapter Settings,
right-click your internet connection and select Properties.
Click the Sharing tab, check “Allow other network users to connect.”. choose your virtual Wi-Fi adaptor
May 12th, 2011
From Nmap Manual
If you find yourself really bored one rainy afternoon, try the command
nmap -Pn -sS -p 80 -iR 0 –open
to locate random web servers for browsing.
(use it at your own risk !! as some companies might complain for port scanning)
March 1st, 2011
Like most administrators, you’ve probably received a call from a user complaining that the network was “slow.” The good news is that with TPing you can monitor network latency, set maximum thresholds, and resolve problems before your users complain. Understanding your network, its performance, and its problems often requires a suite of tools that allows you to examine various aspects of your network. This tool provide solid data that let you baseline your network, troubleshoot problems, and measure anomalies and improvements.
TPing is a network monitoring tool written in Python. It uses its own low level socket programming to send ICMP ECHO_REQUEST to a host or device. With each collection, it sends 1 pings to get the latency. Results are then displayed in real-time so you can monitor network latency.
TPing can be used to continuously monitor a number of servers, routers, workstations, or other devices and continually show real-time response rates.

TPing is a simple console based utility that allows you to view ping results in a console window, TPing can even track the network latency high/low limit recorded during the sample period.
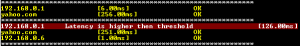
(Click on the image to view full scale)
The TPing network latency application has the ability to concurrently store network latency results in a log file for later review and analysis.
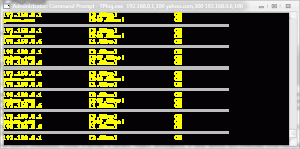
The different colors are a function of packet loss. Yellow means life is good; red means you’ve got troubles.
Please download the TPing Package from here TPing and extract in same folder
For executing TPing (with Administrative Rights), syntax is :-
TPing.exe IP,MaximumLatency IP,MaximumLatency and so on
e.g. TPing.exe 192.168.0.1,100 yahoo.com,300 google.com,200
Incase of VC2008 Dlls missing error you might need to download & Install VCRedist package from here vcredist_x86
January 26th, 2011
You might heard about Application‐level DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks on websites such as Twitter, Facebook and Wikileaks. Usually those kind of attacks involves a large number for HTTP/HTTPS requests to specific part of the website that could potentially eat up all the resource of the server resulting unresponsive behavior from the web server.
There are already some tools available to shut down any website and make it unreachable for legitimate users.
Looking at the technique used to perform this attack, the tool sends about 10 Long HTTP/HTTPS requests per second until it reaches bandwidth or connection limits of the hosts or networking equipment to make it offline.
Now the question is how we can stop this attack? What are the preventive measures against the Layer7 DDoS?
First of all, we start limiting the traffic using hashlimit on iptables. This module can be used to allow just a certain number of packets per minute:
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -m hashlimit --hashlimit-upto 50/min --hashlimit-burst 20 --hashlimit-mode srcip --hashlimit-name http -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j DROP
where "–hashlimit-burst 20" is the burst limit, you can adjust as per your requirement.
Also using Apache you can add a module mod_reqtimeout. This directive can set various timeouts for receiving the request headers and the request body from the client.
Hope this helps…
December 21st, 2010
Here are some of my Linux bash shell findings, I hope it is good for everyone
Find some text in current folder, sub-folders and files:-
find . | xargs grep 'string_to_find'
Getting current time from some time server:-
cat < /dev/tcp/time.nist.gov/13
Convert Unix Timestamp (aka Epoch):-
date -d @1292946804
Tue Dec 21 20:53:24 2010
Downloading a URL:-
exec 5<>/dev/tcp/www.net.cn/80
echo -e "GET / HTTP/1.0\n" >&5
cat <&5
Sending Data over network:-
cat /etc/passwd > /dev/tcp/example.com/10000
TCP Port Checker:-
(echo >/dev/tcp/127.0.0.1/23) 2>/dev/null \
&& echo open || echo close
And
cat < /dev/tcp/localhost/25
Smallest Port Scanner:-
#!/bin/sh
# Usage:>$PortScanner.sh hostname_or_ip startport endport
for ((i=$2; $i <=$3; i++)); do
echo >/dev/tcp/$1/$i && echo $i/tcp Port Open;
done 2>/dev/null
Making File Backup when working on it
cp portscanner.sh{,.bak}
“!$” Reusing Last command arguments
mkdir /path/to/exampledir
cd !$
Taking Folder Backup with rsync (local)
rsync -Aax myfolder/ myfolder-dirbkp_`date +”%Y%m%d”`/
Deleting all files/Folder except some (in this example data and config folder will not delete)
ls | grep -v ‘(data)|(config)’ | xargs rm -r
Will add more tricks laters…..